Why Western Union Loses in AI - Argentina Case Study
An AI Visibility analysis reveals: How ChatGPT, Gemini & Claude interpret Argentina's money transfer market – and why local reality is completely absent
Executive Summary
This case study analyzes how AI systems—ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude, and Perplexity—interpret three money transfer brands operating in Argentina: Western Union, Wise, and Prex. Using Waikay.io's AI knowledge graph analysis, we reveal a fundamental disconnect between market reality and AI understanding.
Key Findings: Western Union dominates with 30 knowledge citations but loses in commercial recommendations (only 5 citations vs. Wise's 7). Prex, despite 27 knowledge citations, has zero commercial visibility—AI miscategorizes it as a prepaid card, not a transfer service. Wise, with the fewest knowledge citations (26), wins AI recommendations due to superior semantic clarity and structured content.
The Argentina Leak: Due to missing local sources, AI systems compensate with off-topic documents—UN PDFs, Supreme Court pages, climate reports—creating a semantically unstable knowledge space where local realities (dólar blue, BCRA regulations, transfer limits) are completely absent.
Strategic Implication: In AI-mediated markets, visibility depends not on brand strength but on semantic clarity, structural documentation, and consistent local content. This study provides a framework for understanding and improving AI visibility in markets where global brands lack local information architecture.
Table of Contents
- I. Why This Case Study?
- II. Methodology: How AI Visibility Was Measured
- III. How AI Describes the Three Brands (LLM Answers)
- IV. Sources View: The Convergence Map
- V. Topic Map: Which Semantic Spaces AI Connects
- VI. Commercial Intent: Who Dominates "Best Platform" in AI?
- VII. The Argentina Leak: Why AIs Suddenly Cite Government Sites and UN PDFs
- VIII. Comparison of the Three Brands
- IX. Strategic Interpretation of Results
- X. Conclusion & Action Recommendations
I. Why This Case Study?
Introduction & Objective
International money transfer services are among the most widely used digital services in Argentina—a country characterized by intense currency volatility, strong regulations, and high demand for international remittances.
Yet while users clearly search for reliable platforms, a second, far more decisive filter operates in the background:
How do AI systems interpret these brands?
The Invisible Competition
Modern LLMs (ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude, Perplexity) answer thousands of questions daily such as:
- "What's the best platform for sending money?"
- "How does Wise work in Argentina?"
- "Is Western Union cheaper than Xoom?"
What determines visibility is not actual brand quality, but rather:
→ Which sources the AI uses for its world knowledge
→ Which brands dominate in its internal knowledge graphs
This case study examines precisely this mechanism.
The Brands Under Analysis
| Brand | Domain | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Western Union | westernunion.com | Global market leader |
| Wise | wise.com | Digital challenger |
| Prex | prexcard.com.ar | Local player |
The Central Questions of This Study
Visibility:
- Which domains do AI models cite most frequently?
- How do the models describe these brands?
Semantic Spaces:
- Which topics are linked to these brands?
- Where are the semantic gaps?
Market Dominance:
- Which players dominate the Argentine semantic field?
- Why are some brands nearly invisible?
Methodology
For this analysis, we used Waikay.io (developed by Dixon Jones). This tool reveals the "AI Knowledge Graph Sources"—the domain clusters on which LLMs build their answers.
Analyzed AI Models:
- ChatGPT
- Google Gemini
- Anthropic Claude
- Perplexity
First Central Finding
There are massive differences between:
✗ Global brand presence
✗ Actual AI world knowledge
AI systems cite knowledge from entirely different sources than one would intuitively expect.
What This Means
Even established brands can, in AI responses:
- Be described incorrectly
- Appear in the wrong context
- Be completely absent
Key Insight
The following chapters demonstrate how and why this happens—and what companies can learn from it. We'll examine the specific knowledge sources AI systems rely on, analyze the semantic relationships they've formed, and reveal the strategic implications for brands operating in AI-mediated markets.
II. Methodology: How AI Visibility Was Measured
This case study is based on a structured analysis of three international money transfer brands that are active or relevant in Argentina:
- Western Union – westernunion.com
- Wise – wise.com
- Prex – prexcard.com.ar
All three brands were examined using a standardized AI Visibility analysis, focusing on two core questions:
- How do AI systems interpret these brands?
- On which domains and sources does the AI build its knowledge?
2.1 Comparison Model
To ensure comparability, both global and local versions of the domains were considered:
| Brand | Global Domain | Local Domain (Argentina) |
|---|---|---|
| Western Union | westernunion.com | westernunion.com/ar/es |
| Wise | wise.com | wise.com/ar |
| Prex | — | prexcard.com.ar |
Why this approach?
International brands often deliver contradictory signals (global vs. local). LLMs mix this information—and this analysis makes that process visible.
2.2 AI Models Used
The evaluation encompasses four of the most important LLM ecosystems:
- ChatGPT (OpenAI)
- Google Gemini
- Anthropic Claude
- Perplexity / Sonar
All models were tested with the same question set and identical comparison parameters to identify answer consistency and source usage.
2.3 Analysis Tool: Waikay.io
For the evaluation, we used the tool Waikay.io (developed by Dixon Jones).
What Waikay.io Reveals:
| Analysis Dimension | What Is Measured |
|---|---|
| Sources View | Which domains an AI uses for knowledge formation |
| Topic Reports | Which topics a model recognizes as relevant |
| Commercial Queries | Which brands dominate in transactional questions |
| LLM Answers | How the AI describes each brand |
Important: Waikay.io is not an SEO tool—it measures whether a brand exists in the AI's world knowledge, is cited, or is completely ignored.
2.4 Analysis Focus
The entire report concentrates on a single guiding question:
Guiding Question
How does AI interpret the three brands Western Union, Wise, and Prex in the Argentine context?
Examined Aspects:
Source Structure:
- Which domains are used as knowledge sources?
- How often is each brand cited in Knowledge Queries?
Commercial Visibility:
- How often does each brand appear in Commercial Queries?
- Which brand is preferred in "best platform" questions?
Semantic Gaps:
- Which information do AI systems mix or lose?
- Which semantic gaps lead to misinterpretations?
- Which off-topic sources does the AI draw on when information is missing?
What the Methodology Reveals
This analysis goes beyond classic SEO. It doesn't show how brands rank in search engines—but rather how AI systems understand, categorize, and recommend brands.
That is the decisive difference.
III. How AI Describes the Three Brands (LLM Answers)
This chapter is not about rankings, not about sources, not about convergence maps.
It's about one thing only:
How AI models describe the three brands when asked about them directly.
And this is precisely where the discrepancy becomes extremely clear.
3.1 Western Union: Global Player – But Weak AI Description
Tested Domains:
- westernunion.com
- westernunion.com/ar/es/home.html
Result: All AIs deliver extremely generic answers—regardless of the Argentine version.
Typical AI Statements About Western Union:
✓ "200+ countries"
✓ "145 years of experience"
✓ "Money transfer worldwide"
✓ "Send · Receive · Tracking"
✓ "Security features"
✓ "Mobile app available"
What's Completely Missing:
✗ Argentina-specific fees
✗ Dólar Blue / parallel exchange rate
✗ BCRA regulation
✗ Problems with the WU app in Argentina
✗ 24h availability (often incorrect in reality)
✗ Cash pickup reality (agents without cash)
Interpretation
Western Union is the most-cited player (30 Knowledge Citations), but the AI doesn't understand how Western Union actually functions in Argentina.
The LLM profile is: global → generic → decontextualized.
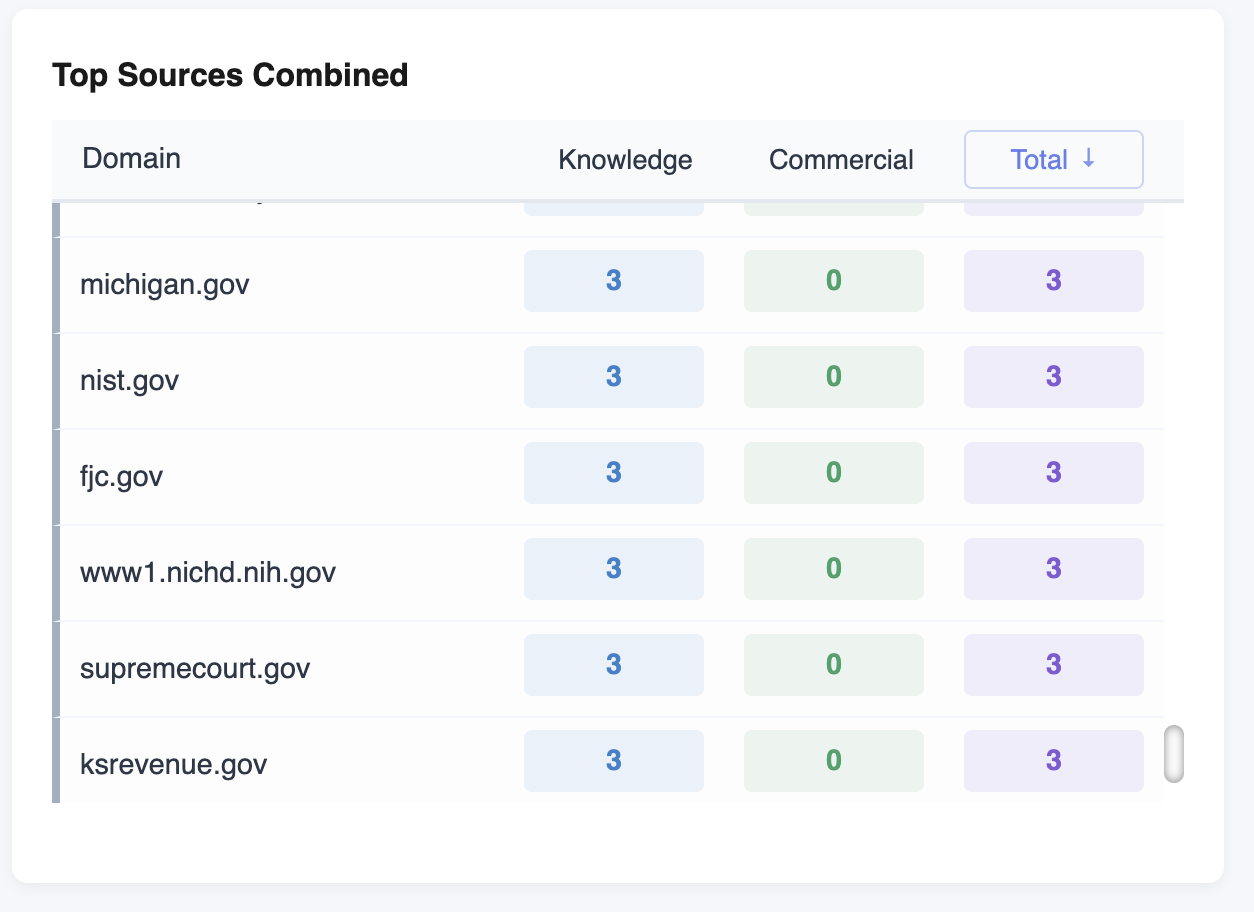
3.1.1 What the Content Gap Analysis Shows
The structured analysis of the Western Union Argentina page confirms the AI interpretation:
Critical Gaps:
- ✗ No information on Cumplimiento Normativo (BCRA/AFIP regulatory requirements)
- ✗ No clear details on Velocidad de Transferencia (transfer speed per destination)
- ✗ Missing pages for Uruguay and Chile (important destinations for Argentine users)
- ✗ No details on Opciones de Divisa (which currencies are available)
Consequence: The AI cannot extract this information—and fills the gap with global standard statements like "200+ countries" instead of local, usable details.
This explains why Western Union has a "global shadow profile" despite 30 Knowledge Citations.
3.2 Wise: Global Digital Brand – Better Understood Than WU
Tested Domain:
- wise.com/ar
Result: The AIs deliver significantly more precise answers than for Western Union.
Typical AI Statements About Wise:
✓ "International transfers at real exchange rates"
✓ "Transparent fees"
✓ "Digital account solution"
✓ "Argentina restricted due to local regulation"
✓ "Modern, transparent, and affordable"
Why Does Wise Appear So Strong?
Wise has a total of 26 Knowledge Citations and is extremely well-documented globally. The brand delivers clear, structured information that AI systems can process well.
But: Many AI answers are based on global information, not on Argentina-specific rules.
Nevertheless: Wise is described more clearly, precisely, and modernly than Western Union—which doesn't reflect the real market relationship, but does reflect AI world knowledge.
3.3 Prex: Local Player – Not Recognized by AIs as a "Transfer Brand"
Tested Domain:
- prexcard.com.ar
Result: Prex is not recognized by AIs as a player in the context of "sending money from Argentina."
Typical AI Statements About Prex:
✓ "Digital prepaid card"
✓ "Fintech solution"
✓ "Local payment functions"
✗ "No clear profile as international transfer platform"
The Problem
Although Prex has 27 Knowledge Citations (almost as many as Western Union!), the AI focus is completely wrong:
- ✗ Not recognized as international transfer solution
- ✗ No mention of fees, limits, exchange rates
- ✗ No connection to "dinero desde Argentina"
Prex exists for AI in the wrong semantic space.
3.4 Comparison of LLM Descriptions (Quick Matrix)
| Brand | AI Description | Quality | Problem |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western Union | global, generic, historical | ⭐ medium | no local reality (Argentine context completely missing) |
| Wise | modern, transparent, digital | ⭐⭐ good | often global info, Argentine context partially incorrect |
| Prex | Fintech/prepaid card | ⭐ poor | AI does NOT recognize Prex as transfer service |
3.5 Why This Matters
These differences in LLM answers reveal the core of the problem:
→ AI doesn't know how money transfer actually works in Argentina
→ Brands are sorted into wrong semantic spaces
→ Local reality is completely absent
→ Globality bias dominates interpretation
3.6 Supplement: What the "Facts" Analysis Shows
Beyond the general LLM answers, the Facts View from Waikay.io shows which "facts" AI models claim about Western Union Argentina.
The Numbers at a Glance:
92 Facts total – divided into:
- 46 Facts about "Enviar dinero desde Argentina"
- 46 Facts about "Western Union Argentina"
At first glance, this seems comprehensive. But the analysis of topics shows a different picture.
Problem 1: Extremely Low Thematic Depth
The most-mentioned topics in both fact sets:
| Topic | Frequency | What This Means |
|---|---|---|
| Argentina | 20x | Geographic mention, but no local details |
| money / money transfers | 17x / 13x | Generic term, no Argentina specifics |
| Western Union | 14x / 19x | Brand name repetition without context |
| website / site | 7x / 16x | Technical mention of domain structure |
| fees | 5x / 4x | Mentioned, but never with concrete numbers |
| exchange rates | 4x | Concept known, but no Blue/MEP/Oficial distinction |
The Problem: These "facts" are extremely repetitive and superficial.
The AI repeatedly lists the same basic information:
- "Western Union enables money transfers"
- "The website is available in Spanish"
- "There are fees"
- "Exchange rates play a role"
But: Not a single one of these "facts" goes into depth.
Problem 2: What's Completely Missing
Not a single fact mentions:
- ✗ BCRA regulations
- ✗ AFIP limits
- ✗ Dólar Blue vs. Oficial
- ✗ RENAPER/CUIT requirements
- ✗ Cepo Cambiario
- ✗ Transfer speed to Argentina
- ✗ Concrete fees in ARS
- ✗ Local payment methods (Rapipago, Pago Fácil)
This confirms: The AI has many citations, but no real understanding of the Argentine context.
Problem 3: Model Inconsistency
Different LLMs recognize different numbers of facts:
| Model | Facts "Enviar dinero" | Facts "Western Union" |
|---|---|---|
| Gemini | 8-11 | 12-11 |
| Claude | 7 | 6 |
| ChatGPT | 10 | 8 |
| Sonar | 10 | 9 |
What This Means
Even the models disagree among themselves on what counts as a "relevant fact."
This is a clear sign of semantic instability—when even AI systems lack consistent interpretation, there's no stable knowledge foundation.
Why Is This Important?
This facts analysis reveals the core problem in three dimensions:
1. Quantity ≠ Quality
→ 92 facts sound like a lot, but they're 92x the same superficial information
2. Globality Displaces Locality
→ The AI knows "Western Union" and "Argentina," but doesn't understand "Western Union IN Argentina"
3. Lack of Consistency Between Models
→ When AI systems don't agree, there's no stable semantic basis
Conclusion of Facts Analysis
AI doesn't understand Western Union in Argentina as a local reality, but as a global standard service—without regional differences.
Thus, the facts analysis fully supports the previous chapters:
✓ LLM answers are shallow
✓ Local context is missing
✓ Semantic spaces are wrongly set
✓ Brands are not understood as "Argentine" services
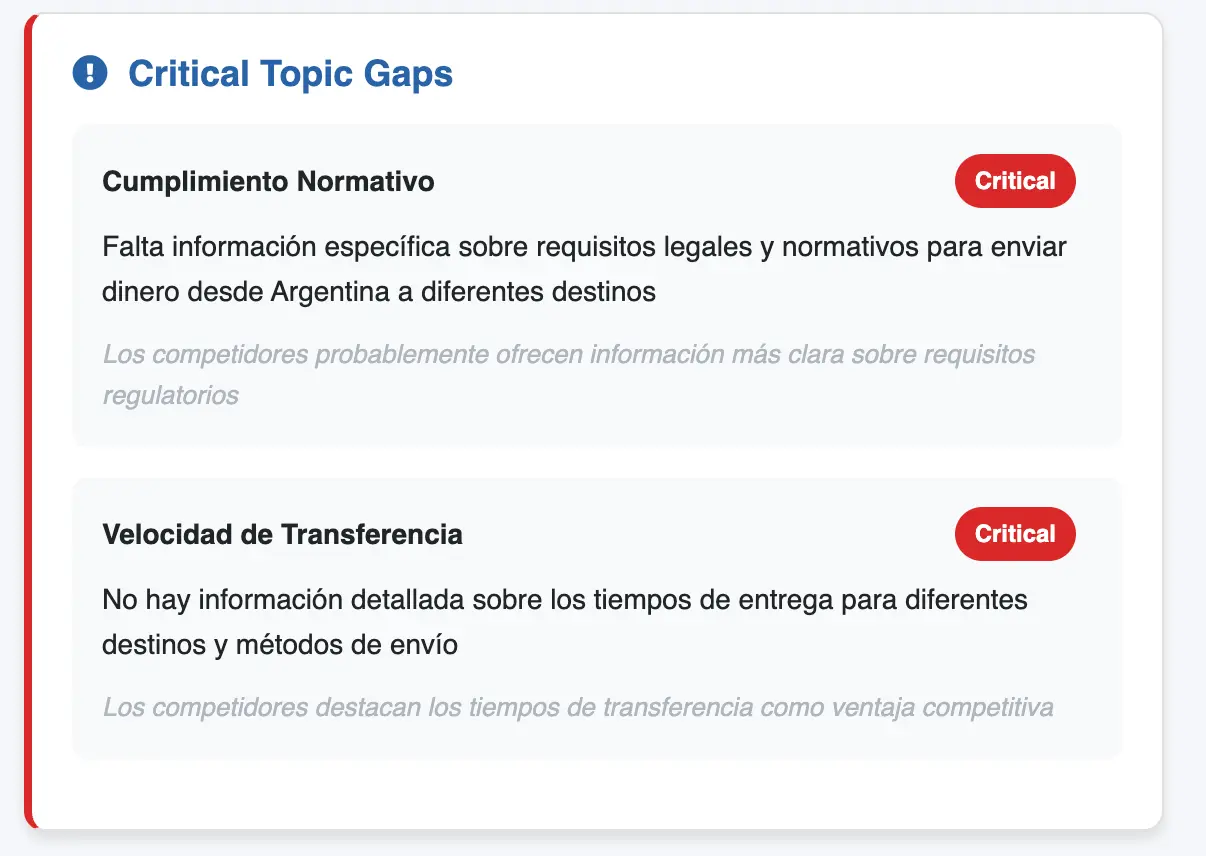
IV. Sources View: The Convergence Map
This chapter is the core of the entire case study.
Here we see how AI structures its world knowledge on the topic "sending money from Argentina"—and why certain brands dominate.
The data is based on the Sources View from Waikay.io. The convergence map shows:
- Which domains the AI uses as knowledge foundation
- How frequently they are cited
- Whether they are Knowledge Sources (blue) or Commercial Sources (orange)
4.1 The Three Dominant Players
Despite different market roles and business models, only three domains dominate the semantic field:
| Brand | Domain | Knowledge Citations | Commercial Citations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western Union | westernunion.com | 30 | 5 |
| Prex | prexcard.com.ar | 27 | 0 |
| Wise | wise.com | 26 | 7 |
Interpretation
Western Union wins in the knowledge area—but the AI uses almost exclusively global sources, not local ones (".ar"). This causes WU to lose the Argentine context.
Wise is comparatively very strong in commercial responses. For "best platform" questions, Wise dominates.
Prex is a local hero with high knowledge presence—but AI doesn't recognize Prex as a competitor in international offerings.
→ Knowledge: yes | Commercial: no
4.2 The Actual AI Dominance Fields (Visual Clusters)
Analyzing the source data reveals three distinct clusters:
1️⃣ Global Money Transfer Cluster
Brands: Western Union, Wise, Xoom, Remitly, Ria
This is the largest cluster. The AI preferentially uses these domains for:
- "How do I send money from Argentina?"
- "Best platforms"
- "Fee comparison"
- "How does Wise/WU/Xoom work?"
Significance: Anyone missing from this cluster doesn't exist for AI as an international transfer solution.
2️⃣ Local Banking / Fintech Cluster
Brands: Prex, MercadoPago, Billeteras Virtuales
This cluster provides knowledge, but no recommendations.
Prex appears 27 times, but is not categorized as a global solution.
→ AI assigns Prex to local payment transactions, not international transfers.
Significance: Local brands are semantically isolated—even when they're internationally usable.
3️⃣ Off-Topic & Confidence Sources
Here lies the most interesting part of the analysis:
The AI compensates for missing, stable Argentine sources with completely off-topic PDFs and government pages.
Examples from the dataset:
- supremecourt.gov
- UN PDFs
- Apple Business Pages
- FTC Consumer Warnings
- IPCC Climate Report
- nist.gov
- library.tamu.edu
What Does This Mean?
When AI finds no strong sources, it replaces missing structure with "Confidence PDFs"—highly-rated documents, regardless of topic.
This is a classic "Argentina leak."
4.3 Why These Clusters Are Decisive
The convergence map reveals three fundamental problems:
Problem 1: Narrow Knowledge Base
AI builds its Argentina knowledge almost exclusively on a few global players:
- Western Union
- Wise
- Prex (local)
- Xoom, Remitly, Ria
- Monito (comparison portal)
All other providers are completely absent.
Problem 2: Semantic Instability
Because local sources are missing, "red cluster" sources mix in.
This happens almost exclusively in markets with:
- High inflation
- Unstable regulations
- Many patchwork solutions
- Fragmented information sources
- Missing official guideline documents
Argentina meets all five criteria.
Problem 3: Missing Reality Recognition
The models don't cleanly recognize what Argentine reality is.
This leads to AI answers that are:
- Incomplete
- Globalized
- Incorrect
- Oversimplified
- Partially hallucinated
4.4 The Most Important Insight from Chapter IV
AI has a clear, unambiguous order:
→ Western Union = global knowledge (Knowledge dominant)
→ Wise = commercial decisions (Commercial dominant)
→ Prex = local financial knowledge (but not a "winner" in recommendations)
This order is the foundation for the later chapters (Topic Map, Commercial Intent, Interpretation).
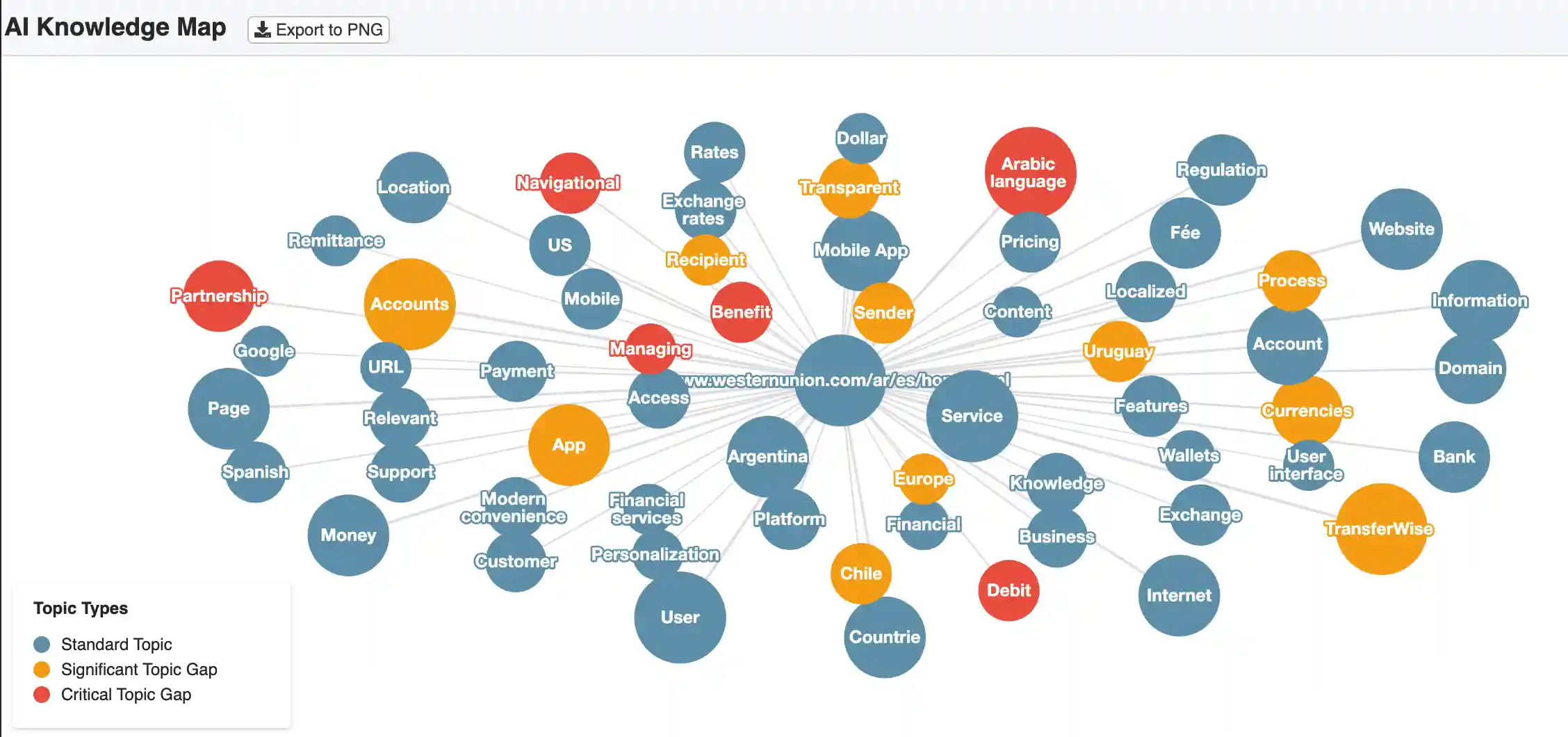
V. Topic Map: Which Semantic Spaces AI Connects
The Topic Map shows how AI models structure the entire market thematically.
Here we see which topics AI classifies as central, important, or secondary—regardless of whether this assessment is correct.
This reveals at a glance:
- Which topics are dominant
- Which topics are missing
- Where false interpretations arise
- How stable or unstable the semantic space "sending money from Argentina" is for AI
5.1 What AI Recognizes as Central Topics
In the Topic Map, certain themes are repeatedly prioritized. These form the semantic foundation on which AI builds its answers:
Central Topics (blue = Knowledge Domains):
- Send Money / Money Transfer
- Transferencias Internacionales
- Cómo enviar dinero desde Argentina
- Exchange Rates ARS/USD
- Remesas / International Remittances
- Dólar Blue / Dólar paralelo
Why These Topics Dominate:
These topics are globally well-documented and have many stable sources. They shape the semantic space—even if they don't correctly reflect local realities.
Problem: The AI treats Argentina like any other market—even though the reality is fundamentally different.
5.2 What AI Does NOT Recognize (Critical Gaps)
Here the problem begins—and this is precisely what makes this case study valuable.
Critically Missing Topics (red = Missing Knowledge):
| Missing Topics | Why This Would Be Important |
|---|---|
| Argentine Regulation | AFIP limits, anti-money laundering restrictions, identity verification |
| Daily Transfer Limits | Real usability of services |
| Digital Identity | RENAPER, CUIT/CUIL – central for Argentina |
| Local Payment Methods | Mercado Pago, Rapipago, Pago Fácil |
| Onboarding Processes | How does registration actually work? |
| Specific Fee Models | Argentina-specific costs |
| Argentine Banks | Correspondent banks, local partnerships |
| Exchange Rate Realities | MEP, Blue, Tarjeta – three parallel systems |
These Gaps Explain:
→ Why AI overvalues Wise
→ Why AI reduces Western Union to global facts
→ Why AI doesn't interpret Prex as a transfer service
→ Why AI includes off-topic sources (UN, PDFs, SupremeCourt)
In Other Words
❗ The semantic space "sending money from Argentina" is semantically unstable for AI.
5.3 Why These Gaps Emerge
The AI builds its Topic Map from the interaction of four source types:
- Stable Sources (Knowledge)
- Commercial Sources (Commercial)
- Local Sources (Local Knowledge)
- Global Norms (Universal Concepts)
Since there are only few clean local sources, three effects emerge:
A) Global Topics Are Overweighted
The AI insists on universal terms like "Remittances" and "Send Money"—because these terms have stable, global sources.
Consequence: Argentina-specific terms like "cepo cambiario" or "dólar MEP" are completely absent.
B) Local Reality Is Underweighted
Important Argentine topics are completely missing from the graph—not because they're unimportant, but because they are insufficiently documented.
Consequence: AI doesn't "invent" new concepts—it can only reproduce what's in its sources.
C) AI Compensates for Gaps with Off-Topic Documents
→ Exactly the off-topic sources described in Chapter IV.
Consequence: The AI draws on UN PDFs, government pages, and climate reports—not because they're relevant, but because they appear "trustworthy."
5.4 Why the Topic Map Is Central to This Case Study
The Topic Map answers the question:
Core Question
"What reality does AI believe about Argentina?"
And this reality is currently:
❌ Global
❌ Generic
❌ Stable (but wrong)
❌ Barely localized
❌ Free of regulatory details
❌ Compensated with partial information gaps
This Means Concretely:
✓ AI doesn't understand Argentina
✓ AI prioritizes global brands because they provide the most stable sources
✓ Local providers like Prex don't exist in the global context
✓ Western Union is recognized as a global player, but not as a local market leader
✓ Wise is often portrayed above its actual market weight
What This Means for Companies:
If your brand is not anchored in the central topics of AI, it doesn't exist for AI answers—even if you're the market leader.
The Topic Map determines visibility.
VI. Commercial Intent: Who Dominates "Best Platform" in AI?
While "Knowledge Queries" show which sources AI draws on for facts, the Commercial Intent area reveals something different:
Core Question
Who AI trusts for purchase-relevant questions.
Typical Commercial Queries:
- "Which is the best platform for sending money?"
- "Which fees are lowest?"
- "How do I compare X with Y?"
- "Which app is most reliable?"
This is where real competition emerges—not for knowledge, but for recommendations.
And the result is clear.
6.1 Dominance in the Commercial Area
Commercial Queries (Number of AI Citations):
| Brand | Commercial Citations |
|---|---|
| Wise | 7 |
| Western Union | 5 |
| Prexcard | 0 |
What This Means:
✓ Wise wins in commercial context
✓ Western Union is visible but loses relevance
✓ Prexcard plays no role in "best-of" answers
6.2 Why Does Wise Dominate?
Despite a smaller global market share, Wise delivers exactly what AI systems are looking for:
What Wise Does Right:
✓ Clearly structured landing pages
✓ Transparent fees (always visible, always comparable)
✓ Global comparison tables ("Wise vs. Western Union")
✓ Strong semantic signals for "low fees," "international money transfer," "best way to send money"
For AI Systems, Wise Is an "Easy Case":
- Clear facts
- Few contradictions
- Good semantic density
- Strong internal linking
- Clear commercial signals
That's why Wise is preferred for questions like "best platform."
6.3 Why Does Western Union Lose Despite Market Leadership?
Western Union possesses:
- Strong global brand authority
- Long history (145 years)
- Massive offline presence
But AI sees something different:
What's Missing at Western Union:
❌ Generic texts ("200 countries," "145 years") instead of concrete benefit communication
❌ Hardly any local details about Argentina
❌ Little context on fee structure
❌ Few modern semantic signals
❌ Very global rather than local optimization
This causes AI to "know" WU but not interpret it as the best option.
6.4 Why Is Prexcard Completely Invisible?
AI doesn't recognize Prexcard as:
- International player
- Money transfer solution
- Commercial alternative
- Recommendation candidate
Why?
Problem 1: Wrong Categorization
Prexcard is local, not global → Semantics are "Wallet," not "International Transfer"
Problem 2: Missing Commercial Signals
No pages with "Comparison," "Fees," "Best way to send money"
Problem 3: No International Validation
No international review signals, no stable AI citation
Core Problem
For AI, Prex is a prepaid/wallet brand—not a transfer service.
Result: 0 Commercial Visibility.
6.5 The Structural Logic of AI
AI evaluates Commercial Intent based on the following building blocks:
| Evaluation Criterion | Wise | Western Union | Prex |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fee Comparison | ✓ | ○ | ✗ |
| Reliability Signals | ✓ | ✓ | ○ |
| Easy Explainability | ✓ | ○ | ✗ |
| Global vs. Local Reach | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ |
| Stable Source Base | ✓ | ○ | ○ |
| Total | 5/5 | 3/5 | 1/5 |
Interpretation:
Wise meets all five criteria → Rank 1
WU meets three → "Okay, but not the best option"
Prex meets one at most → "No recommendation"
6.6 Brief Conclusion on Chapter VI
This chapter shows:
✓ Who dominates recommendations in the AI ecosystem
✓ Why Wise appears as "best platform"
✓ Why WU loses despite size
✓ Why Prex is commercially invisible
The Decisive Point
Recommendations don't emerge from brand status, but from semantic clarity.
What This Means for Companies:
Even market leaders can lose in AI recommendations—when their content:
- Is too generic
- Offers no clear comparison points
- Doesn't reflect local realities
- Sends no modern semantic signals
VII. The Argentina Leak: Why AIs Suddenly Cite Government Sites and UN PDFs
When you first see the source map, something immediately stands out:
Critical Observation
Why do completely irrelevant domains suddenly appear?
Examples from the Data:
- supremecourt.gov
- nist.gov (cryptography certificates)
- earthday.org
- UN documents / PDFs
- IPCC climate report
- Apple Business Pages
- library.tamu.edu
This seems chaotic—but it's a highly relevant signal.
7.1 What This "Leak" Means
These off-topic sources don't emerge randomly. They emerge because the AI, on the topic:
"Sending money from Argentina"
finds no stable, relevant, consistent primary sources.
This is a typical case of semantic instability.
The AI Attempts to Compensate for What's Missing
When enough genuine sources are missing, the model does three things:
1. Fallback to trustworthy, global documents
→ Government sites, UN, academic libraries
2. Search for structured PDFs
→ Regulatory metadata, security certificates, general "compliance documents"
3. Replacement of missing contexts with global standards
→ US regulation instead of AR regulation
The Central Mechanism
The AI doesn't understand Argentina—so it compensates with what it perceives as "stable."
This is the Argentina Leak.
7.2 Why This Happens More Strongly in Argentina Than in Other Countries
Argentina has three characteristics that fundamentally confuse AIs:
1️⃣ Complex Currency System Without Documentation
Argentina has multiple parallel exchange rates (Peso, Blue Dollar, MEP, Tarjeta), but neither Western Union nor Wise explain these on their Argentine pages.
The AI cannot distinguish between:
- Official Dollar
- Dólar Blue
- Dólar MEP
- Dólar Tarjeta
—not because these concepts change rapidly, but because no reliable source documents them in a structured, AI-readable way.
2️⃣ Missing Official Digital Knowledge Sources
Only a few reliable sources explain:
- Fees
- Limits
- Regulation
- Travel statutes
- Identification (RENAPER)
- Foreign exchange controls
Problem: Even official entities (BCRA, AFIP) have hardly any structured, AI-readable documentation.
3️⃣ Many Contradictory Information Sources
- Blogs say A
- Media says B
- Banks say nothing
→ AI doesn't know what "ground truth" is.
In such markets, the model "flees" to stable, global PDFs—even when they're thematically wrong.
7.3 What This Leak Reveals About the Entire Market
Core Finding
The semantic space "sending money from Argentina" is undersupplied.
This Means Concretely:
Problem 1: Too little high-quality, structured content
Problem 2: Local players (like Prex) provide hardly any context
Problem 3: Global players provide only generic info
Problem 4: Argentina-specific facts are missing almost everywhere
Problem 5: There's no single actor providing clean knowledge signals
This Is Why the AI:
✗ Describes Western Union incorrectly
✗ Miscategorizes Prex
✗ Overestimates Wise
✗ Doesn't recognize important local factors at all
7.4 Why This Leak Is One of the Strongest Insights of the Entire Case Study
Because it shows:
The brands aren't the problem—the market is.
And even more importantly:
LLMs cannot interpret Argentina when the knowledge space is unstable.
What This Means:
No single company can solve this problem alone—but every company that provides clean, structured, local information gains massively in AI visibility.
Strategic Implication
This is exactly why professional Semantic Market Intelligence matters.
Practical Consequence:
Companies operating in unstable markets like Argentina must:
- Create their own knowledge sources (no expectation that AI will "automatically understand")
- Explicitly document local contexts (BCRA limits, fees, processes)
- Send consistent signals (not contradictory info on different pages)
- Provide structured data (Schema.org, FAQs, clear comparison tables)
Otherwise, UN PDFs and climate reports fill the semantic gap.
VIII. Comparison of the Three Brands (Western Union, Wise, Prex)
This chapter summarizes the most important findings of the analysis.
The three providers—Western Union, Wise, and Prex—show completely different visibility patterns in AI systems. Contrary to their market size or local popularity, they are understood, weighted, and categorized differently by AI models.
To make the results tangible, here is a clear comparison table across all relevant dimensions.
AI Visibility Matrix – Tabular Comparison
| Analysis Dimension | Western Union | Wise | Prex |
|---|---|---|---|
| Knowledge Sources (citations in knowledge queries) | 30 citations | 26 citations | 27 citations |
| Commercial Sources (citations in commercial queries) | 5 citations | 7 citations | 0 citations |
| LLM Recognition (brand profile) | Very generic, global, barely any Argentina reference | More precise, functional, clear advantages in answers | Not recognizable as money transfer service |
| Topic Depth | Low – AI mentions standard facts ("200 countries") | Medium – better explanations of fees, speed | Very low – AI often confuses or doesn't recognize Prex |
| Local Knowledge (Argentina-specific) | Weak – almost no local specifics | Moderate – partially local info | Very weak – AI doesn't understand role & offering |
| Entity Stability (brand stability in AI knowledge graph) | High – but global, not local | Medium – clear classification | Low – unstable, often misclassified |
| Commercial Ranking | Inferior despite market size | Dominant | No relevance |
| AI Interpretation Quality | "Global shadow profile" – no Argentina depth | "Functional profile" – good answers | "Dead profile" – barely usable answers |
Brief Contextualization of Results
1) Western Union – Visible, But Misinterpreted
WU has the most Knowledge citations, but AI interprets the brand almost exclusively from global sources.
Consequence: The LLMs deliver extremely generic, superficial answers without local context.
Diagnosis: Global Shadow Profile
→ The brand is present, but not understood
2) Wise – Smaller, But Commercially Dominant
Wise has the most commercial citations (7).
This means: AI recommends Wise more frequently in answers with purchase or comparison intent.
In Argentina, this creates an asymmetric overpresence.
Diagnosis: Functional Profile
→ The brand is understood and preferentially recommended
3) Prex – Local Player Without AI Relevance
Prex receives many Knowledge citations (27)—but: AI doesn't recognize Prex as a money transfer provider.
Thus, Prex has no Commercial Impact (0 citations).
Diagnosis: Dead Profile
→ The brand exists but is miscategorized
Interpretation: What the Table Really Means
The matrix shows three fundamentally different AI profiles:
Western Union: Visible, But Imprecise
→ Knowledge is global, not local
→ High presence, low relevance
Wise: Functionally Dominant
→ Higher probability in ranking or "best platform" answers
→ Lower presence, higher conversion probability
Prex: Practically Invisible
→ Despite local significance, Prex plays no role for AI
→ High presence, but wrong category
What This Means in Practice
The table shows: AI visibility is not equal to AI relevance.
- Western Union is often cited but rarely recommended
- Wise is cited less often but recommended more frequently
- Prex is often cited but misunderstood
Key Insight
What matters is not the number of citations—but how AI interprets the brand.
This comparison is the link between the analytical chapters (IV-VII) and the strategic contextualization in the next chapter.
IX. Strategic Interpretation of Results
This chapter summarizes what the AI data really means.
It's no longer about numbers, scores, or tables—but rather:
Core Question
How semantic spaces emerge in AI systems and why the Argentine market is particularly unstable in the AI context.
9.1 How AI Forms Semantic Spaces
LLMs don't work with "keywords," but with concept spaces.
A concept space emerges from three layers:
1. Primary Sources (Dominant Sources)
→ Domains that are frequently cited
→ Determine the foundation of world knowledge
2. Secondary Signals (Topics, examples, recurring patterns)
→ Typical terms, narratives, situations
→ Stored as "normal" for a topic
3. Stabilizing Additional Sources
→ PDFs, government sites, reports
→ Used when primary sources have gaps
In the Case of the Argentine Money Transfer Market:
The primary sources are extremely narrow, yet they dominate the entire perception:
- Western Union
- Prex
- Wise
- Ria, Xoom, Remitly (commercial layer)
Thus, AI knowledge inevitably becomes: narrow, distorted, incomplete.
9.2 Why Argentina Is Semantically Unstable
Argentina creates a special problem for AI:
✗ Complex currency system poorly documented by transfer providers
✗ Two parallel exchange systems without clear explanation (official dollar vs. Blue dollar)
✗ Unclear legal situation for transfers—not explained on brand websites
✗ Many unofficial solutions (cuevas, informal exchange houses)—never mentioned
✗ Missing structured information on local regulations
This Leads to Three Structural Breaks in the AI Knowledge Space:
1. Missing Clear Entities
There are no stable, permanent terms and rules.
"Enviar dinero desde Argentina" has different parameters every month.
2. Semantic Gaps in the Market
Neither Western Union nor Wise cover all relevant concepts:
- Límites
- Trabas
- Impuesto PAIS
- 70/30 rule
- Mercado Pago Restricciones
3. Loss of Local Realities
AIs tend to interpret Argentina through "global logic":
→ Stable markets
→ Clear fees
→ Simple banking structures
→ Digital identity = unambiguous
This doesn't work in Argentina.
9.3.1 Example: The Missing Compliance Documentation
The Content Gap Analysis of Western Union Argentina shows the problem concretely:
What's Missing:
- No page on "Cumplimiento Normativo" (BCRA limits, AFIP rules, identity verification)
- No information on transfer speed per destination
- No explanation of currency options (USD, EUR, ARS)
What Happens Then?
The AI finds no reliable source on Argentine regulations and falls back on:
- UN PDFs on international money laundering prevention
- NIST documents on cryptography standards
- FTC Consumer Warnings (US-based)
Answers thus become global instead of local—this is the Argentina Leak in action.
9.3 Why Western Union Is Misinterpreted
Western Union is extremely present in Argentina. However, AI recognizes mainly the global brand, not the local reality.
This Causes the AI to:
✗ List global facts ("200+ countries," "145 years")
✗ Repeat generic security notices
✗ Not know local fee models
✗ Not consider AR-specific restrictions
✗ Not describe real user journey
Key Problem
AI doesn't describe Western Union as an Argentina platform, but as a global, general company.
Thus, WU loses local technical competency points.
The Strategic Context: Western Union has relied on pure offline dominance in Argentina for years: branches, physical presence, local agencies. Digital visibility was never prioritized, as the market was considered digitally underdeveloped. A global website was deemed sufficient—not only in Argentina, but in many emerging markets. In traditional web search systems, this strategy still worked, but in AI search engines it leads to massive visibility loss: the brand exists everywhere offline, but semantically almost not at all online.
9.4 Why Prex Appears Strong But Isn't Recommended
Prex appears strongly in Knowledge Sources because:
✓ The domain provides many structured contents
✓ The pages are technically clean
✓ The brand appears entity-stable (clear thematic focus)
BUT:
Prex is not primarily an international transfer solution.
AI doesn't always recognize this clearly. An overweighting in the knowledge space emerges that doesn't correspond to reality.
This is called: Entity Over-Attribution.
9.5 Why Wise Wins Despite Smaller Knowledge Base
Wise works excellently internationally. AI "loves" Wise because:
✓ The domain has extremely many structured financial contents
✓ International logic is consistent
✓ Fee transparency is clearly communicated
The Problem:
Wise can only be used to a limited extent in Argentina. However, AI adopts international narratives—without local restrictions.
This leads to a misinterpretation of usability.
9.6 Why Local Realities Are Completely Missing
No AI mentioned in answers:
| Missing Concepts | Argentine Reality |
|---|---|
| dólar blue | Parallel currency |
| impuesto PAIS | Tax burden on transfers |
| cepo cambiario | Foreign exchange restrictions |
| restricciones del BCRA | Regulatory limits |
| cuevas | Informal exchange houses |
| límites por CUIT | Identity-based limits |
| métodos informales | Real user practices |
| reales diferencias de tarifas | Hidden costs |
| AR-specific identity verification | RENAPER, CUIT/CUIL |
| Volatility within 24h | Exchange rate chaos |
This Shows
The semantic space "sending money from Argentina" is insufficiently modeled. No clean knowledge foundation exists.
9.7 Consequence: Context Loss + Topic Gaps = Wrong Answers
AI answers seem plausible at first glance. But they're based on:
✗ Global knowledge
✗ Missing AR context
✗ Incomplete source clusters
✗ Wrong priorities
✗ Compensating off-topic documents
This Leads to Systematic Misinterpretations:
- Incorrect fee comparisons
- Ignored regulations
- Overestimation of global players
- Underestimation of local solutions
- Erroneous "best platform" recommendations
9.8 Conclusion of This Chapter
The data clearly shows:
Core Finding
Artificial intelligence doesn't understand the Argentine money transfer market—it reconstructs it from global fragments.
This Explains:
→ Why Western Union is misrepresented
→ Why Prex appears too strong
→ Why Wise is overestimated
→ Why the market remains semantically unstable
→ Why off-topic PDFs appear
→ Why local realities are missing
→ Why AI recommendations are often wrong in Argentina
What This Means for Companies:
In semantically unstable markets like Argentina, brand strength doesn't determine AI visibility—but rather:
- How clearly the brand is documented
- How consistent the signals are
- How well local realities are reflected
- How stable the source structure is
This chapter provides the strategic foundation for the action recommendations in Chapter X.
X. Conclusion & Action Recommendations
The analysis of the three brands—Western Union, Wise, and Prexcard—clearly shows how AI systems currently categorize the money transfer market in Argentina.
Two global players (WU, Wise) and one regional provider (Prexcard) form the core of AI answers, although the real market is much more diverse and numerous other services are active.
The Central Finding
Core Conclusion
Artificial intelligence knows only a small segment of the actual market—and structures its knowledge based on few, recurring sources.
This creates a distorted picture:
- Global brands appear more stable than they actually are in Argentina
- Regional providers like Prexcard are partially miscategorized
- Other services don't appear at all, despite being used in practice
This Leads to Three Consequences:
1️⃣ AI Answers Are Heavily Simplified
They orient themselves to the best-known domains and deliver generic descriptions that barely address local rules, restrictions, or everyday user problems.
2️⃣ Knowledge About Argentina Is Primarily Derived From Global Sources
This means:
- Fees, limits, regulation, peso logic, or dólar blue are barely understood
- Models replace missing context with international PDFs, government sites, or random off-topic sources
- This creates gaps or even clear misinterpretations
3️⃣ Market Interpretation Remains Incomplete
Even established players—whether local or international—are only considered in AI answers when stable, recurring sources exist.
For many services, this is not the case.
Concrete Action Recommendations: Western Union Argentina Example
The Content Gap Analysis shows what's missing—and what must be built:
Phase 1: Content Creation (High Priority)
1. Create Regulatory Clarity
- Create "Cumplimiento Normativo" page
- Document BCRA limits
- Explain AFIP requirements
- Describe RENAPER/CUIT identity verification
2. Complete Missing Destinations
- Create pages for Uruguay
- Create pages for Chile
- Create pages for Peru
3. Increase Transparency
- Document transfer speed per destination
- Clearly present currency options (USD, EUR, ARS, Blue?)
- Present payment methods clearly
Phase 2: Structural Improvements
1. Hub Page "Envíos desde Argentina"
- Visual overview of all destinations
- Filter options (speed, cost, method)
- Comparison table for different destinations
2. Local FAQ Section
- "¿Cómo funciona con el dólar blue?"
- "¿Cuáles son los límites mensuales?"
- "¿Qué documentos necesito?"
Phase 3: Semantic Optimization
1. Implement Structured Data
- Schema.org for financial services
- FAQ markup for common questions
- Breadcrumb navigation
2. Consistent Terminology
- Uniform terms across all pages
- Use local terms (cepo, dólar MEP, BCRA)
Expected Result
These measures would help Western Union transition from a "global shadow profile" to a "functional profile"—like Wise currently has.
Measurable Goals:
• Increase Commercial Citations from 5 to 10+
• Improve topic depth
• Reduce off-topic sources in Argentina context
What Companies Can Learn From This
1. AI Needs Stable, Clear Brand Signals
Without clear page structures, unambiguous explanatory pages, fee comparisons, local guides, and recurring mentions, no reliable brand image emerges.
Concrete:
- FAQ pages with structured data (Schema.org)
- Comparison tables (Wise vs. Western Union)
- Local landing pages with specific information
- Consistent terminology across all channels
2. Local Specifics Must Be Explicitly Explained
Especially in countries like Argentina, clear, well-documented presentation is crucial:
| What Must Be Documented | Why |
|---|---|
| Limits | Daily/monthly transfer limits |
| Identity Verification | RENAPER, CUIT/CUIL requirements |
| Payment Methods | Mercado Pago, Rapipago, bank transfers |
| Currency Logic | Official rate vs. Blue vs. MEP |
| Risks & Fees | Transparent cost breakdown |
Important: AIs don't automatically learn from this—this information must be actively accessible.
3. International Players Should Strengthen Local Sub-Pages
Western Union is an example:
Strong global presence, but weak local AI profile → leads to generic answers.
Solution:
- Argentina-specific content pages
- Local blog posts on regulations
- Fee calculator with ARS/USD/Blue
- User stories from Argentina
4. Regional Providers Must Make Their Role Visible
Prexcard is an example:
Widespread in Uruguay and partly in Argentina—but AI doesn't recognize the international utility.
Solution:
- Clear positioning as "international transfer solution"
- Comparison pages ("Prex vs. Western Union")
- Use cases for cross-border payments
- External validation (reviews, media mentions)
What This Case Study Means for marcus-a-volz.com
This case study clearly shows how large the gap between real market and AI knowledge can be—especially in complex markets like South America.
And This Is Precisely Where the Opportunity Lies:
Helping companies build their brand knowledge so that AI systems:
- Understand them (correct categorization)
- Correctly classify them (right semantic spaces)
- Reliably cite them (Knowledge + Commercial Queries)
The Service Portfolio From This:
1. AI Visibility Audits
→ How do AI models currently interpret your brand?
2. Semantic Gap Analysis
→ What knowledge and topic gaps exist in your market?
3. Market Intelligence for AI Systems
→ How do you structure content so AI understands it?
4. Local Knowledge Frameworks
→ How do you build local expertise that AI can interpret?
5. Commercial Intent Optimization
→ How do you position yourself in "best platform" answers?
This Makes It Clear:
Strategic Conclusion
AI interpretation has long been a competitive factor—especially in markets that are complex, volatile, or poorly standardized.
Closing
If your organization wants to understand how AI models interpret your brand across different countries and platforms—and how to strengthen this visibility—feel free to reach out.
I help companies build a clear, reliable presence in markets where traditional SEO signals are no longer enough.
Marcus A. Volz
Semantic Market Intelligence
marcus-a-volz.com